histone modifications|how does histone modification work : iloilo Histone modifications are dynamically added and removed from histone proteins by specific enzymes (table 2). The balance between these writers and erasers dictates which marks are present on histones, and at what levels, to ultimately control whether . See more WEB11 de fev. de 2022 · Técnico da Itália desde 1977, Enzo Bearzot reuniu o que de melhor o futebol do país oferecia para desempenhar um bom papel na Copa de 1982. Depois de levar a Itália ao quarto lugar na Copa de 1978 apresentando um bom futebol, Bearzot fez jogadores como Scirea e Tardelli despontarem como craques na Azzurra, com muita .
0 · regulation of chromatin by histone modifications
1 · list of histone modifications
2 · how does histone modification work
3 · histone modifications types
4 · histone modifications and gene expression
5 · histone modification database
6 · histone methylation vs dna
7 · histone acetylation vs methylation
8 · More
webPesquise reputação de empresas antes de comprar. Se tiver problema, reclame e resolva rápido. Toda empresa tem problema, boa é aquela que resolve.
histone modifications*******Learn about the nine types of histone modifications, such as acetylation, methylation, and phosphorylation, and how they regulate gene expression and chromatin structure. Find out how to study histone modifications by ChIP and use Abcam's products and services. See more
Histone modifications are dynamically added and removed from histone proteins by specific enzymes (table 2). The balance between these writers and erasers dictates which marks are present on histones, and at what levels, to ultimately control whether . See more
Histone modifications regulate the physical properties of chromatin, and its corresponding transcriptional state, either directly (eg acetyl . See moreBarski, A., Cuddapah, S., Cui, K., Roh, T.Y., Schones, D.E., Wang, Z., Wei, G., Chepelev, I., and Zhao, K. High-resolution profiling of histone . See morehow does histone modification work Histone modifications exert their effects via two main mechanisms. The first involves the modification (s) directly influencing the overall structure of chromatin, .histone modifications how does histone modification work Histone modification enzymes like HAT, HMT, HDAC and HDM's basic function is to regulate gene expression. For example, histone methylation often results . Histone post-translational modifications (PTMs) have been mainly regarded as instructing DNA-templated processes. In this Review, Gonzalo Millán .Histones. Epigenetics is the epi-information beyond the DNA sequence that can be inherited from parents to offspring. From years of studies, people have found that histone . Recently, histone tail cleavage by various enzymes is regarded as an alternative modification to remove pre-existing tail modifications but retaining the . Abstract. In eukaryotic cells, DNA is tightly packed with the help of histone proteins into chromatin. Chromatin architecture can be modified by various .
Histone modifications such as acetylation and methylation are somewhat complex. These modifications are differentially implicated in neuron development and .
This histone modification is deposited by the polycomb complex PRC2. It is a clear marker of gene repression, and is likely bound by other proteins to exert a repressive . The correlation between histone modifications and transcriptional regulation dates back to pioneering work by Allfrey, Mirsky and colleagues, which demonstrated that histone lysine acetylation . In particular, six emerging classes of histone H3 modifications are subjected for epigenome profiling by the International Human Epigenome Consortium. In general, transcription start sites of .Histone writers, erasers, and readers in cancer. Histone H3 tail lysine residues, frequently subject to posttranslational modifications (PTMs), are indicated along the left side. The typical distribution of these H3 PTMs is also indicated along the length of gene loci (including distal enhancers) as shaded blocks.
histone modifications Histone modifications also function as epigenetic passengers that can be inherited by daughter cells to maintain lineage-specific transcription profiles 2. Thus, understanding functions of histone . Histone modifications such as acetylation and methylation are somewhat complex. These modifications are differentially implicated in neuron development and disease; some active or repressive marks globally increase or decrease, respectively, during these processes. In other cases, gene-specific changes in histone . Histone modifications are key epigenetic regulators that control chromatin structure and gene transcription, thereby impacting on various important cellular phenotypes. Over the past decade, a growing number of studies have indicated that changes in various histone modifications have a significant influence on the aging . Abstract. In eukaryotic cells, DNA is tightly packed with the help of histone proteins into chromatin. Chromatin architecture can be modified by various post‐translational modifications of histone proteins. For almost 60 years now, studies on histone lysine acetylation have unraveled the contribution of this acylation to an open .
Histones serve to both package and organize DNA within the nucleus. In addition to histone post-translational modification and chromatin remodelling complexes, histone variants contribute to the . Histone methylation, which usually occurs at the lysine (K) residues of histone H3 and H4 by adding methyl groups, is one of the most important post-transcriptional modifications [].This methylation is catalyzed by the histone methyltransferase (HMT), which uses S-adenosyl methionine (SAM) as the substrate to .
Histone modifications are regulated by chromatin ʻwritersʼ (methyltransferases, for methylation), which add modifications; ʻerasersʼ (demethylases, for methylation), which remove modifications .Histone modification is a fundamental epigenetic regulator that plays a crucial role in various essential cellular processes. This process involves the modification of histone proteins through several types of chemical changes, including acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, and ubiquitination, which commonly occur on the amino-terminal .
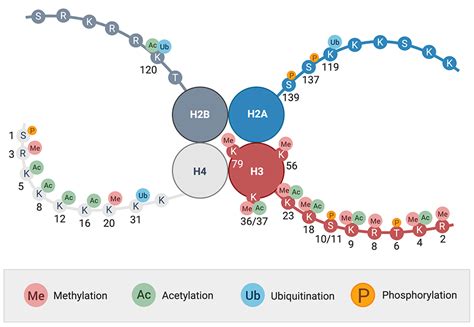
Histone acetylation.Acetylation is shown as an example of a posttranslational modification of histone proteins. A Connolly surface model with secondary structures of histone H3 (a) is displayed in combination with a zoom into its amino-terminal tail.The positively charged amino acids lysine (K) and arginine (R) are .
Middle: The histone (H3
These findings suggest that gene-specific changes in histone modifications may be more important than global histone modifications in modulating the expression of key genes associated with hypoxia.Learn about the most common histone modifications eg H3K4me3, H3K9me3, and H3K27me3 and their readers, writers, and erasers. Histone modifications exert their effects via two main mechanisms. The first involves the modification(s) directly influencing the overall structure of chromatin, either over short or long.
After the histone translation, its amino tail undergoes various modifications, such as methylation, acetylation, phosphorylation, ubiquitination, malonylation, propionylation, butyrylation, crotonylation, and lactylation, which .From years of studies, people have found that histone modifications, DNA methylation, and RNA-based mechanism are the main means of epigenetic control. In this chapter, we will focus on the ge . This article reveals cross-talk between RNA and histone modifications and thus bridges epitranscriptomics and epigenetics. Histone modifications (e.g., acetylation, methylation, crotonylation, and serotonylation) and other epigenetic regulators (e.g., histone variants) are involved in embryonic neurogenesis.
Here, we describe the known histone modifications, define where they are found genomically and discuss some of their functional consequences, concentrating mostly on transcription where the majority of characterisation has taken place.

Histone modifications. Epigenetic modulation involves changes in the activity and expression of chromatin that include variations such as methylations and histone modifications [29]. Similarly, many aging-related effects are caused by chromatin changes.Histone modifications. Epigenetic modulation involves changes in the activity and expression of chromatin that include variations such as methylations and histone modifications [29]. Similarly, many aging-related effects are caused by chromatin changes.
Resultado da Confira os selecionados do Seleçao Inglesa em BeSoccer e descobre que jogadores foram convocados
histone modifications|how does histone modification work